|
The origin of human genetic variability from
cross-species comparisons: The truth about Blast
The strategy of comparing human SNPs and chimpanzee sequences
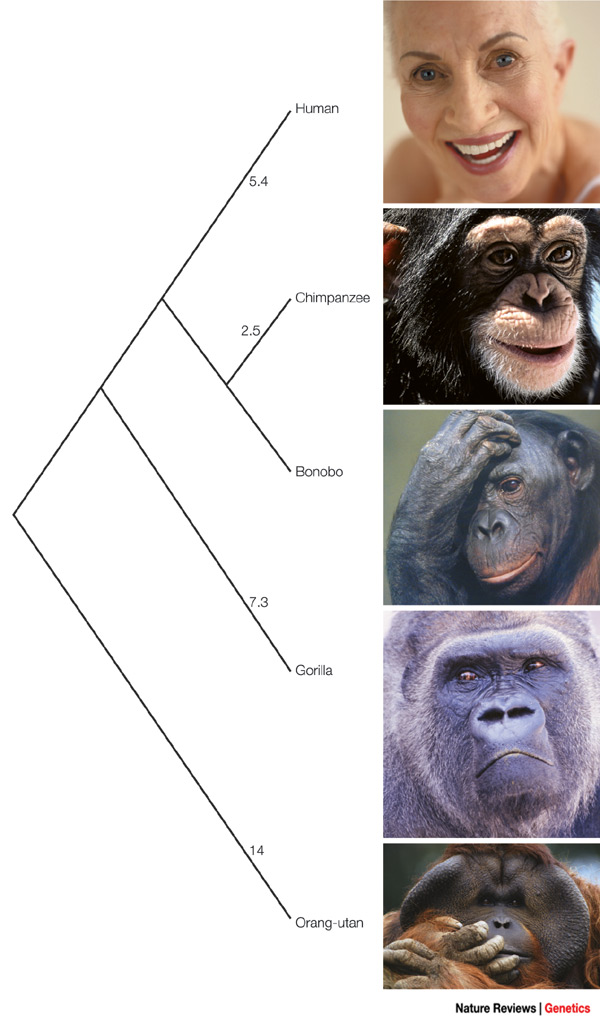
The chimpanzee genomic sequence is the best resource for inferring the ancestral allele of any human SNPs. The average sequence divergence between human and chimpanzee genomes is approximately 1.2%. Therefore, most of the SNPs which can be mapped in the human genome are likely to be mapped in the chimpanzee genome as well.
To map a SNP to the human or chimpanzee genome sequences is essentially the same as to search a DNA sequence in the genome. However, there are some specific requirement due to the nature of the SNPs and their flanking sequence. It requires that:
- SNP position is within the aligned region
- nucleotide where SNP site matches has to be one of the two alleles of the SNP
- at least 100 bp in length
- at least 95% similarity between the flanking sequence and the matched genomic sequence.
Back to main Scenario page back one page continue
|